New construction of piping systems requires some type of cleaning of debris or contaminants. Debris can be defined as substances such as dirt, grease, construction materials such as wood, wire, hard hats, tools, weld slag, rust and scale, and any other small objects that could be misplaced inside the diameter of piping systems. Proper cleaning of Piping Systems is required dependent upon service requirements.
Piping System Cleaning Requirements
All piping systems shall be flushed with water. Water flush is accomplished through the hydro-testing of piping systems. If the water being drained still has evidence of debris, continue to flush with water until no evidence of debris exists.
Lines that require cleaning should be identified on the Mechanical Flow Diagrams. The Process Engineering Group (Process Department) shall set the limits based on the service requirements and equipment being protected from debris and contaminants generated during construction.
Certain process services require chemical cleaning of Piping Systems. The process engineer shall be responsible for identifying services that require chemical cleaning. Typical examples of services requiring chemical cleaning are listed below:
- Reciprocating Compressor suction piping
- Super High-Pressure Boiler Feed Water and High-Pressure Steam
- Product Shipping Lines
- Specialty Chemical /Catalyst lines
- Oxygen
- Hydrogen Peroxide
The designer should be responsible for verifying all steps to remove debris that would be detrimental to the process fluid, including the provision of any temporary facilities for carrying out the chemical cleaning procedures.
The cleaning method used should be selected based on the facilities available. Steam and detergent cleaning is much less costly than acid or mechanical cleaning. Each project specification must indicate the type of contamination/debris to be removed.
All systems shall be sealed after cleaning to keep out dirt and moisture. Cleaning in place with chemical cleaning solutions shall be compatible with all components of the piping system; otherwise, components that would be adversely affected by the cleaning solution shall be temporarily removed.
The use and disposal of cleaning solutions must be in accordance with plant policy or local regulations (or both).
Types of Pipe Contamination for Stainless Steel
- Dirt
- Iron contamination
- Grease and loose weld spatter
- Scale and tight weld spatter
- Oil, paint, or grease
- Rust
Types of Pipe Contamination for Carbon Steel
- Dirt
- Varnish or protective oil
- Mill scale
- Shop weld spatter and scale
- Rust
- Moisture (low-temp service)
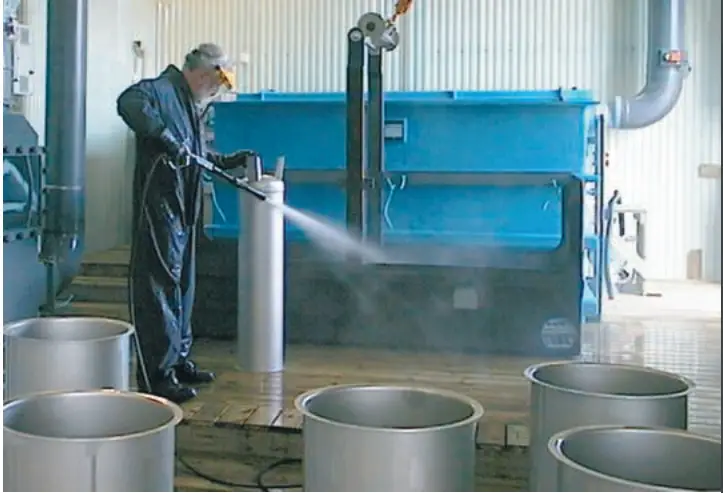

Various types of Piping Cleaning
Mechanical Cleaning: Rotating shafts, brushes, compressed air, and flying grit are hazards. Use protective equipment dictated by the site.
Chemical Cleaning: Acids and other chemicals, heated solutions, steam pressure hoses, spills, and sprays are hazards. Provide protective clothing, eye protection, safety showers, and facilities to neutralize spills of spent chemicals. Personnel should not breathe ferroxyl solution (or other chemicals) vapors that may be harmful. Adequate respiration must be provided when testing or cleaning in enclosed areas with inadequate ventilation.
Vapor Cleaning: Steam, condensate, and other hazards are associated with chemical cleaning. Controlled discharge of vapors to the atmosphere or condensate cooled by water sprays is essential to minimize personal contact.
Pipe Cleaning procedures
Procedure for Water Flush:
- Flush the pipe with chloride-free clean water.
- Thoroughly drain the pipe and dry it if required. Drying can be done by wiping or by blowing with clean, dry compressed air or inert gas.
Procedure for Air Blow:
- Blow with clean, dry compressed air. Use a sufficient volume of air to create high velocity in the pipe.
Procedure for Steam and Detergent Cleaning:
- Steam-clean with a water solution of Pennwalt Corp. Cleaner MC-79, Oakite Products, Inc. Oakite 33, or approved equal. (Mix 1 gal MC-79 with 9 gals clean water; mix 1 gal Oakite 33 with 6 gals clean water.)
- Drainpipe thoroughly and flush with clean water.
- Dry the pipe by wiping or by blowing with clean, dry compressed air or inert gas.
Procedure for acid Cleaning for Stainless Steel:
The choice of acid cleaning solution depends upon the composition, heat treatment, and form of the stainless steel to be cleaned. Choose the acid-cleaning solution as follows:
- For mill products or castings in the solution-annealed condition of Type 300 or 400 series and Carpenter 20 Cb (UNS N08020), Alloy B (UNS N10001), or Alloy C-276 (UNS N10276) material, or to weldments, mill products, or castings of CF-8, CF-8M, CF-3, CF-3M, and SW20M (CN-7M): use a nitric-hydrofluoric acid.
- For weldments of Type 304, 316, or any of the other non-extra low carbon (ELC), non-stabilized grades, or for severely sensitized items (such as those that have been stress-relieved) of any of the grades (including ELC and stabilized): use a weak acid.
Procedure for Pickle (Sulfuric Acid method) for Carbon Steel:
- Pickle with a solution of one part Metclean No. 1 or equivalent (inhibited sulfuric acid) 3 to 10 parts of clean water. Heat and maintain the pickling bath between 71 and 82 °C (160 and 180 °F).
- Pump the solution through the pipe or immerse the pipe in a pickling tank until clean.
- Flush with clean water.
- Inspect and repeat steps 2 and 3 if necessary.
- Rinse with a neutralizer solution.
- Dry as required by the process in which the pipe is being used.
Procedure for Pickle (Citric Acid Method) for Carbon Steel:
- Pickle in a solution of 3-1/2 gal of water per lb of citric acid (required anhydrous granular citric acid). Heat and maintain pickling solution between 82 and 88 °C (180 and 190 °F).
- Pump the solution through the pipe or immerse the pipe in a pickling tank until clean.
- Flush with clean water.
- Inspect and repeat steps 2 and 3 if necessary.
- Rinse with a neutralizer solution of 5.0 percent soda ash (Na2CO3).
- Flush with rust inhibitor consisting of 0.5 percent sodium nitrite (NaNO2), 0.25 percent disodium phosphate (Na2HPO4), and 0.25 percent monosodium phosphate (NaH2PO4).
- Dry as required by the process in which the pipe is being used.
Procedure for Mechanical Cleaning for Stainless Steel:
- Blast-clean inside of pipe and fittings with clean, iron-free sand or alundum grit. Repeat if free iron is found. Use ferroxyl test if required. Blast-cleaning of clad material should not be carried to the point of seriously reducing the cladding thickness.
- Walnut-shell blast provides very smooth interior surfaces. Blast inside of pipe and fittings until desired results are obtained.
- For brush cleaning, use stainless steel wire
- Note: Anyone, or all, of the mechanical cleaning procedures, may be required to effectively clean stainless steel pipe and fittings when weld spatter or scale (or both) have formed from welding.
Procedure for Mechanical Cleaning for Carbon Steel:
- Blast clean inside of pipe and fittings. Wire brushing with power rotary wire brushes is an alternate method. A rotary cutter followed by wire brushing should be used on heavily rusted, pitted, and weld-spattered pipe, and on the pipe with a tightly adhered scale.
- Blow out residues with clean, dry compressed air.
- Click here to know more about the internal cleaning of the piping system








Dear,
Do you have procedure for cleaning Titanium Pipe
Dear Anup,
What a noble effort to educate person like me?
Absolutely fantastic..
Thank you so much
Vivek Kulkarni
Good site blog Anup.
One question? For cleaning with steam lines pipe between Flanges we used blind as per Asme B16.48. In one side the blind we used (steam) applied metal rod for oulet steam and debris material inside pipes.
The answer is? This elements is used in others installations facilities?
José
Dear
Our plant, in condenser cooling water pipe inside 25mm thick (very hard) scaling is formed. Can we remove the scale online or offline without affecting the system?